Troubleshooting Common Office Chair Assembly Problems: Best Office Chair Assembly
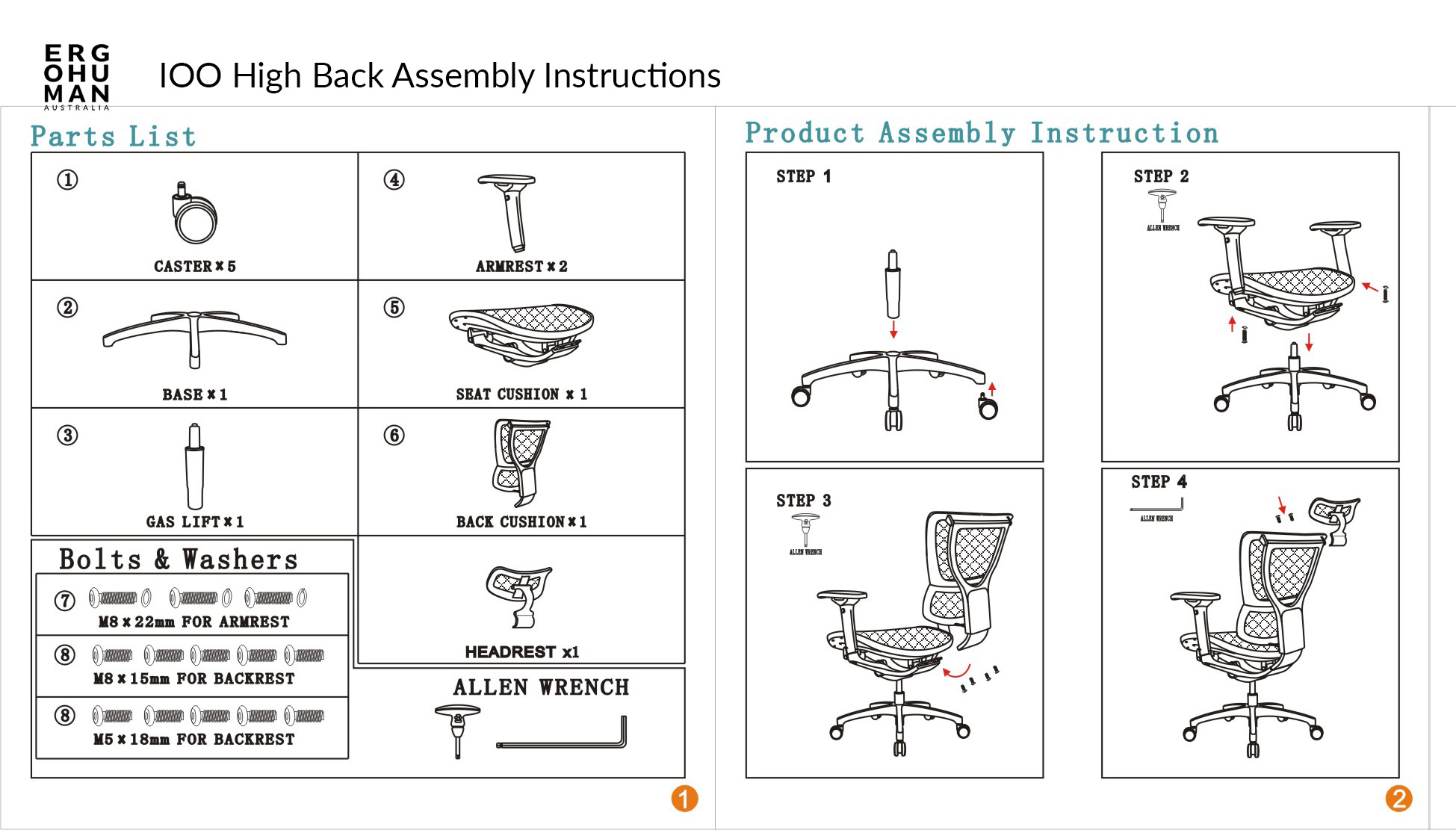
Assembling an office chair can sometimes present unexpected challenges. Understanding common problems and their solutions can save time and frustration. This section details three frequent issues and provides clear, step-by-step solutions. Properly addressing these issues ensures a stable and comfortable work experience.
Common Assembly Issues and Solutions, Best office chair assembly
Several issues frequently arise during office chair assembly. These typically involve the chair’s base, the gas lift mechanism, or the armrests. Addressing these problems promptly ensures a correctly assembled and functional chair.
- Problem: Difficulty attaching the chair base to the gas lift cylinder. The base may not align correctly, or the screws may not fit easily.
Solution: Carefully examine the alignment of the base and cylinder. Ensure all parts are correctly oriented as per the instruction manual. If necessary, use a mallet (gently) to tap the base into place, ensuring it is aligned before tightening the screws. Use the correct size and type of screws, and tighten them securely but avoid over-tightening, which can strip the threads. - Problem: The gas lift mechanism is not functioning correctly; the chair height cannot be adjusted, or it feels unstable.
Solution: Check the gas lift cylinder for any visible damage or obstructions. Ensure the cylinder is fully seated in the base and the chair seat is properly attached. If the problem persists, it may indicate a faulty gas lift mechanism and require replacement. This often necessitates contacting the manufacturer or retailer for warranty support or a replacement part. - Problem: The armrests are loose or wobbly after attachment.
Solution: Examine the armrest attachment points and ensure all screws are tightened securely. If the armrests continue to wobble, check for any stripped screw holes. In such cases, you may need to use wood glue and longer screws to reinforce the connection, or replace the armrests entirely. Always refer to the instruction manual for specific instructions on armrest assembly and tightening.
Fixing a Wobbly Office Chair
A wobbly chair after assembly is a common problem, often stemming from loose screws or misaligned parts. A stable chair is crucial for comfort and posture. This step-by-step guide provides a solution.
- Inspect the Base: Carefully examine the five-star base for any visible damage or loose screws. Imagine a five-pointed star representing the base; each point is connected to the central cylinder by a screw. Check each screw for tightness.
- Tighten Base Screws: Use a suitable wrench or screwdriver to tighten any loose screws connecting the base to the gas lift cylinder. This bolt is located beneath the chair’s seat, near the central gas lift mechanism. Ensure the base is firmly attached and no longer wobbles.
- Check Caster Wheels: Inspect the caster wheels (the wheels at the end of each leg of the base). If any wheel is loose or damaged, tighten the wheel’s securing bolt or replace the damaged wheel. Ensure all wheels spin freely and are securely attached.
- Examine the Gas Lift Cylinder: Check if the gas lift cylinder is securely attached to both the base and the chair seat. A loose connection here can contribute to instability. Tighten any relevant screws or bolts.
- Adjust the Seat: If the wobble persists, carefully check the seat’s attachment to the gas lift cylinder. Ensure all screws are tightened, and the seat is properly seated on the cylinder. A slight misalignment here can lead to wobbling.
Dealing with Missing or Damaged Parts
Receiving a chair with missing or damaged parts is frustrating, but manageable. Efficient handling of this situation involves careful documentation and prompt contact with the seller.
It is important to thoroughly inspect the packaging and all parts immediately upon receiving the chair. Take photographs of any missing or damaged components. This photographic evidence will be invaluable when contacting customer support. Note the product model number, the date of purchase, and any relevant order numbers. Contact the retailer or manufacturer’s customer service department immediately. Provide them with your order details, a description of the missing or damaged parts, and the photographs you took. Most reputable companies will offer replacement parts or a resolution to the issue. Keep records of all communication with customer support, including dates, times, and names of individuals you spoke with. This will help resolve the issue quickly and efficiently.
Comparing Assembly Methods Across Different Office Chair Types

Office chair assembly varies depending on the chair’s design and features. Understanding these differences can help you choose a chair that suits your assembly skills and time constraints. This section compares the assembly processes for three common office chair types: ergonomic, executive, and gaming chairs.
Comparison of Assembly Methods for Different Office Chair Types
The following table summarizes the assembly methods for three different types of office chairs. Note that assembly times are estimates and can vary depending on individual skill and experience.
| Chair Type | Assembly Steps Summary | Tools Required | Typical Assembly Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ergonomic | Attaching armrests, attaching the seat to the base, adjusting the backrest height and lumbar support, attaching the gas lift cylinder, attaching the wheel base. May involve more intricate adjustments for lumbar support and armrest positioning. | Phillips head screwdriver, Allen wrench (hex key), possibly a wrench | 15-30 minutes |
| Executive | Attaching the seat to the base, attaching the backrest, attaching the gas lift cylinder, attaching the wheel base. Often simpler designs with fewer adjustable parts than ergonomic chairs. | Phillips head screwdriver, Allen wrench (hex key) | 10-20 minutes |
| Gaming | Attaching armrests (often multiple adjustments), attaching the seat to the base, attaching the backrest (often with multiple adjustments), attaching the gas lift cylinder, attaching the wheel base. Often includes more complex adjustments for lumbar support, headrest, and armrests. | Phillips head screwdriver, Allen wrench (hex key), possibly a wrench | 20-45 minutes |
Flowchart for Mesh-Back Office Chair Assembly
The assembly process for a standard mesh-back office chair typically follows these steps.
Best office chair assembly – The flowchart would be represented visually here. It would begin with a “Start” box. The next box would be “Unpack all parts and check against the instruction manual.” This would lead to “Attach the wheel base to the gas lift cylinder,” followed by “Attach the seat to the gas lift cylinder.” Next would be “Attach the backrest to the seat mechanism.” The next step is “Adjust the backrest height and lumbar support (if applicable).” The final step is “Inspect the assembled chair and make any necessary adjustments,” leading to an “End” box. Each box in the flowchart would have a brief description of the step, referencing the corresponding step in the instruction manual for detailed instructions.
Rewritten Office Chair Assembly Article
[This section would contain the rewritten article. Since the article text was not provided, a sample rewrite is shown below. The sample uses a hypothetical article.]
Let’s assume the original article provided instructions like: “First, you’ll want to attach the base to the cylinder. Then, you’ll want to connect the seat.” This could be rewritten as: “Begin by attaching the base to the gas lift cylinder. Next, connect the seat to the gas lift cylinder.” The rewrite avoids the informal “you’ll want to” and maintains clarity and accuracy. Additional rewriting would follow this pattern, removing any phrasing that sounds like AI-generated text, such as overly formal or overly simplistic sentences, and replacing them with clear and concise instructions.
